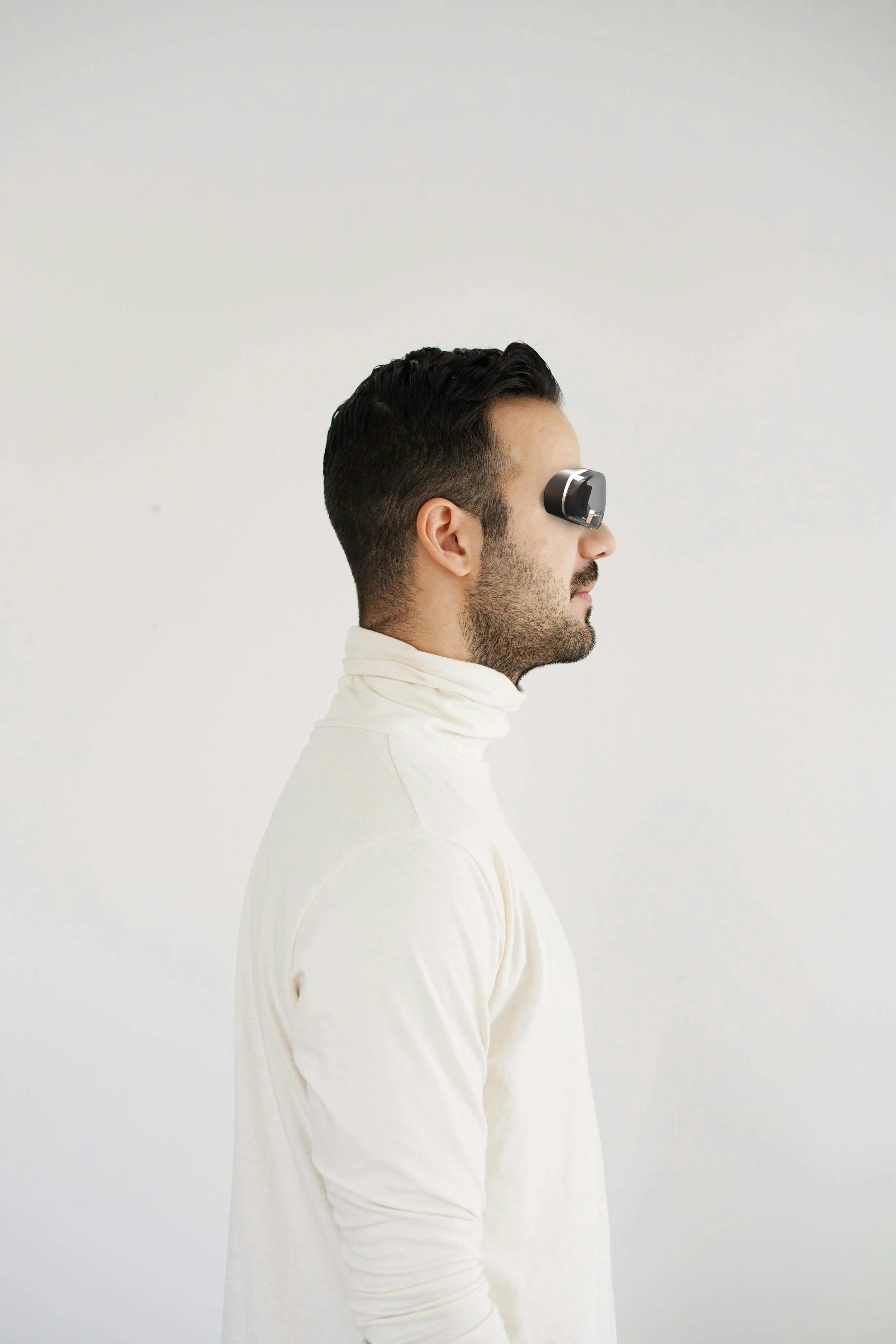
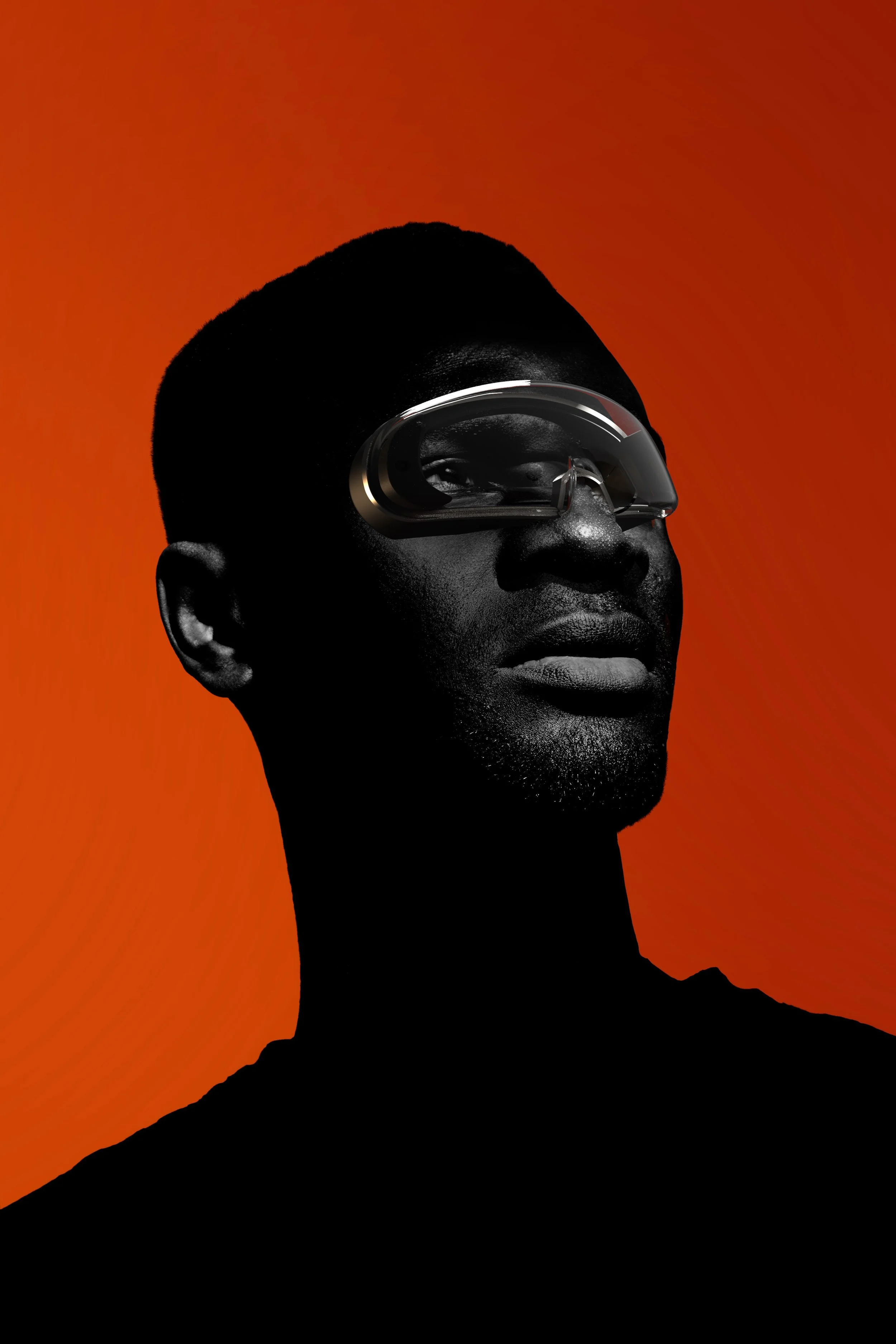
Xsight
Depth Perception at a Glance
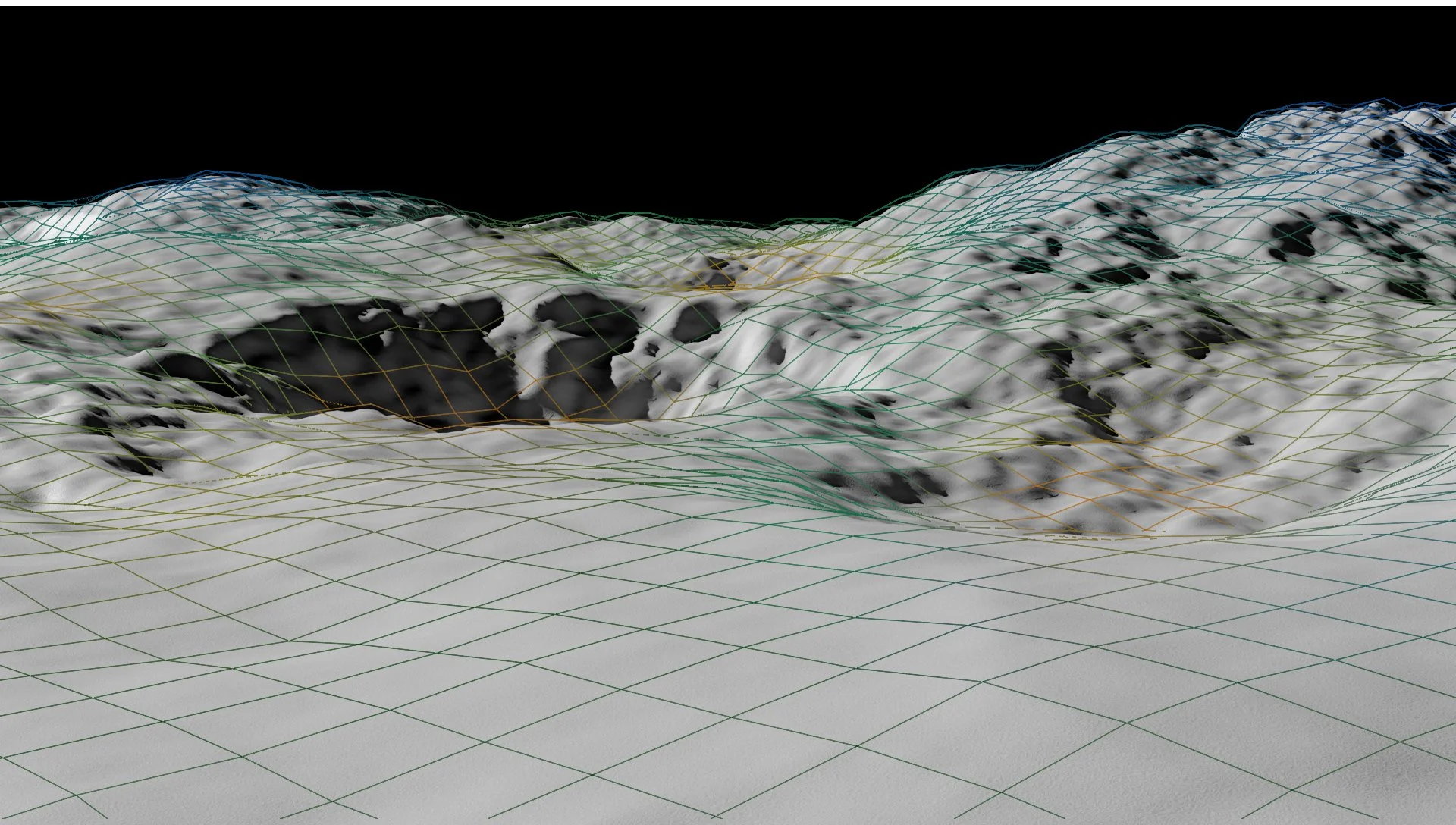
How Did it look for the astronauts?
Approx 100m from House Rock
Astronauts next to House Rock (bottom right)
At first glance the rock formation appeared much closer than it ended up being. Because of this miscalculation almost an hour of time was lost as the astronauts had to navigate themselves to the site. If they had more accurate range finding and depth perception capabilities, they could have saved time, energy, and precious resources.
Apollo 16
On EVA 3 of the Apollo 16 mission, astronauts journeyed to South Ray Crater, home of ‘House Rock’.
Astronauts John Young and Charles Duke parked their lunar rover 100 meters further than they would have if they knew the true size of the formation
-
Single Point laser range finder used to achieve incredibly accurate distance measurements up to 400m with accuracy to 1m
-
A set of six cameras (three on each Fusion module) both tracks the orientation of the headset, and captures a 3D point cloud. With two front facing cameras, they allow for stereoscopic depth perception for wide field tracking.
-
The IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) features a specialized gyroscope, accelerometer, and magnetometer specially tuned for use in space, or on the moon. The IMU handles location and orientation data for the device.
Sensor Fusion System
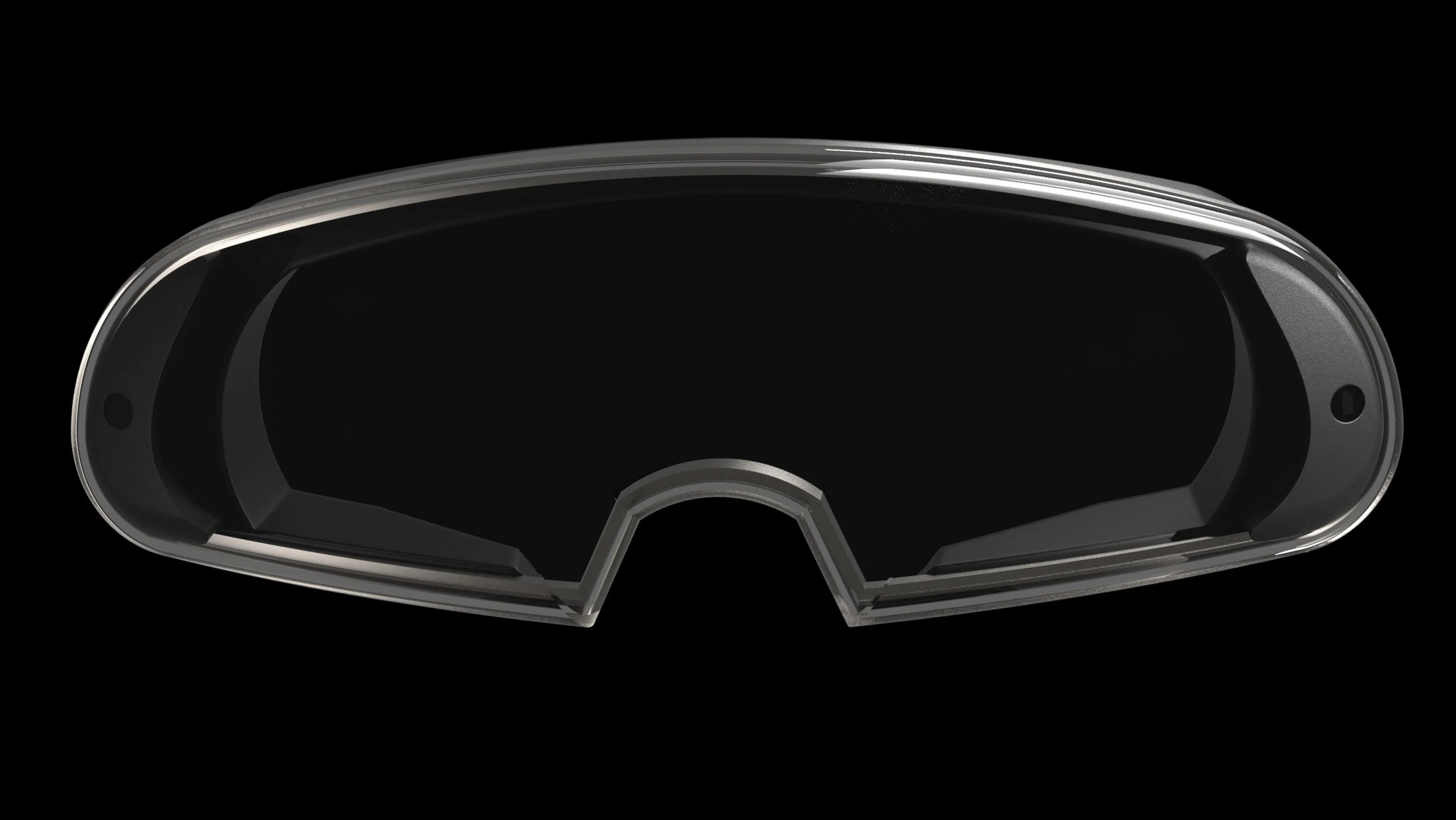
Titanium Frame
Non-toxic Foam
Fusion Sensor Pack
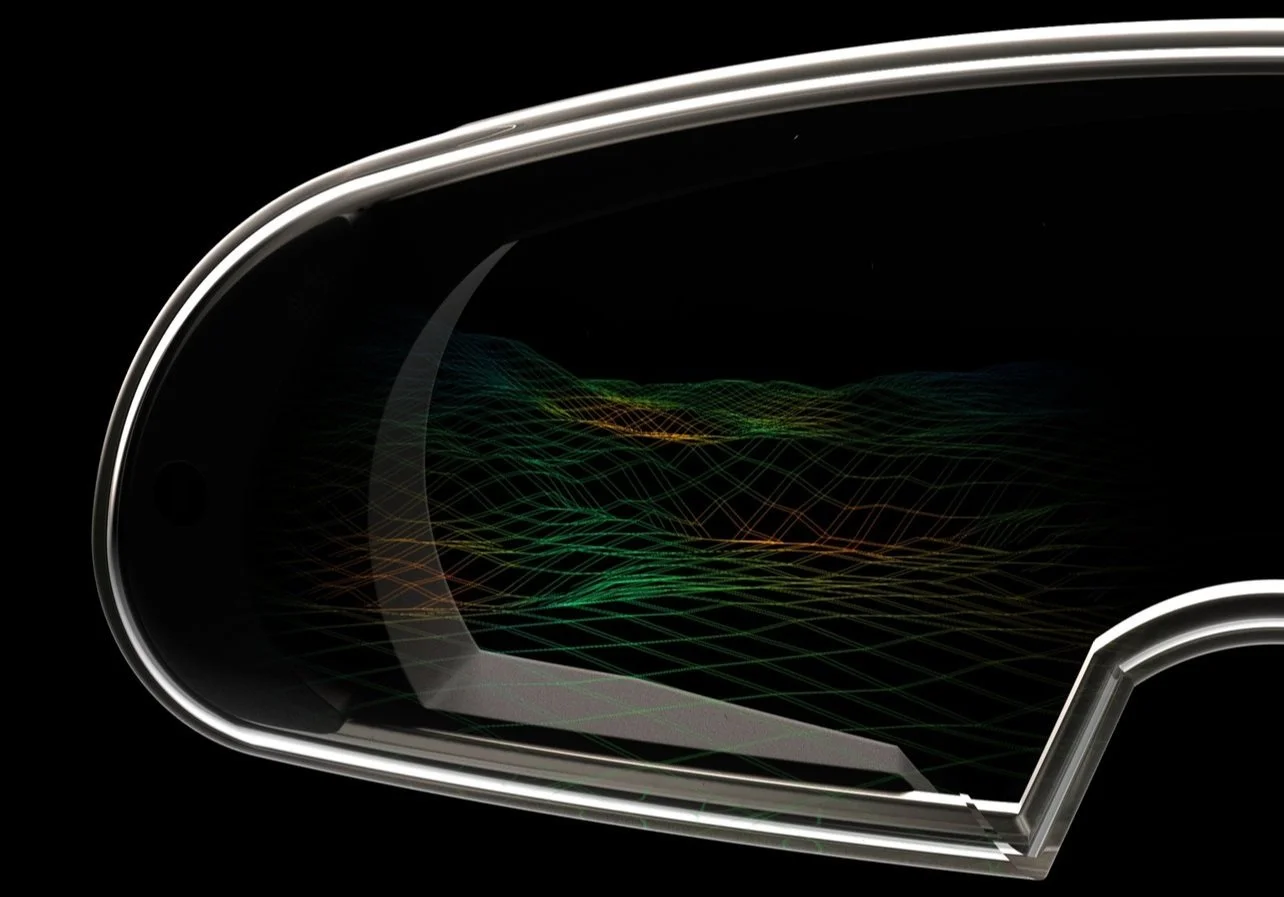
Poly Carbonate Combiner
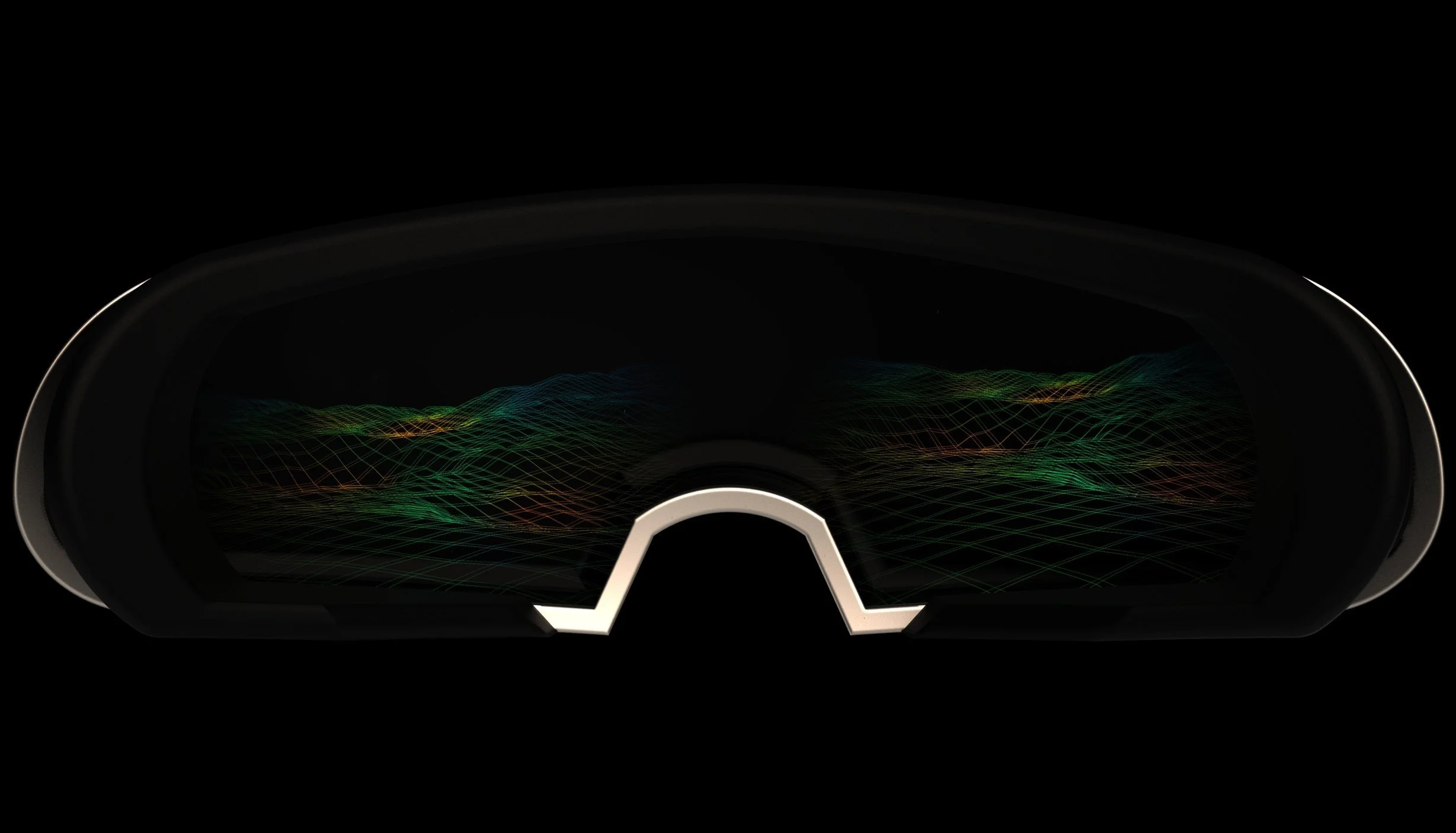
Light Field Projection
Light Field projection allows for accurate depth recreation in the headset by bouncing light rays off of the combiner, and onto the eye of the wearer.